tests for supraspinatus tear|full thickness supraspinatus tear rehab : maker Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder. ESP Reload Neptune’s ESP (Environmentally Sustainable Pack) was the industry’s first pipette reload system designed to minimize plastic waste by 90% and provide an environmentally .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Purpose: Making LB-agar plates where bacteria with an additional plasmid can grow. It is essential to work sterile, thus disinfect your hands and work near a Bunsen Burner. .The autoclave applies high pressure (15 psi) and saturated steam at 121oC (250oF) for 15-20 minutes to kill microbes and spores. After the media has gone through this cycle, it is sterile. Cool to 60-65oC before adding any antibiotics and pouring into sterile Petri .
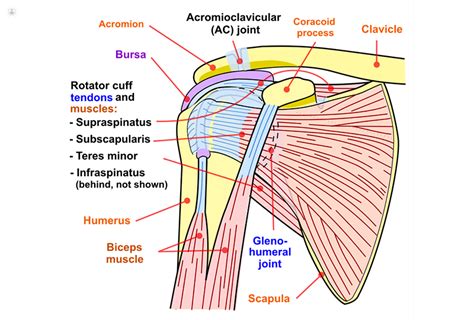
Supraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° .
Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic. Partial thickness: Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres; Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear; Full thickness: Complete disruption of muscle fibresSupraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion.Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body.The results of 5 physical tests used to detect supraspinatus tears, including the hug-up test, EC test, FC test, Neer impingement sign, and Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign were prospectively evaluated.
Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved. In many cases, torn tendons begin by fraying. As the damage progresses, the tendon can completely tear, sometimes with lifting a heavy object. Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis.This page describes the Drop Arm Test, a common test for a supraspinatus tear and/or rotator cuff tear. A video demonstration is included.
Supraspinatus tears are normally present as partial or full-thickness tears. It can be asymptomatic or symptomatic. Partial thickness: Incomplete disruption of muscle fibres; Can progress to complete tear - Increasing pain is normally the first sign of the progression of a tear; Full thickness: Complete disruption of muscle fibresSupraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion.Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus [1]. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body.The results of 5 physical tests used to detect supraspinatus tears, including the hug-up test, EC test, FC test, Neer impingement sign, and Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign were prospectively evaluated.Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved. In many cases, torn tendons begin by fraying. As the damage progresses, the tendon can completely tear, sometimes with lifting a heavy object.
supraspinatus tear pain location
Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis.
special tests for supraspinatus tear
is the sora test hard
is the south carolina permit test hard

shoulder test for rotator cuff
The Amsco Eagle Ten Autoclave is a large capacity, counter-top sterilizer perfect for any size practice. The outside dimensions are compact, saving counter space in the work area. Simply select wrapped, unwrapped, packs or .
tests for supraspinatus tear|full thickness supraspinatus tear rehab